Ways the COVID-19 Pandemic Has Changed Healthcare
Without a doubt, the COVID-19 pandemic has changed healthcare. The uptake in the use of telehealth is but one example.
Chances are you are one of the many people who accessed healthcare via telehealth in the past two years. Telehealth use climbed from less than 1 percent of outpatient visits to 13 percent in the first six months of the pandemic. In the following six-month period, the number declined to 11 percent and ultimately to 8 percent a year into the pandemic.
More recently, we’ve seen more patients utilize telehealth in the midst of COVID-19 surges. In January 2022, for example, as FAIR Health reported, telehealth use climbed for the third straight month during the Omicron surge. “Telehealth utilization increased 10.2 percent, from 4.9 percent of all medical claim lines in December 2021.” As we’ve all come to appreciate, care is everywhere patients go.
Likewise, the uptake of telehealth has meant many changes for providers, particularly in terms of policy and reimbursement. Additional reimbursement changes are likely five months after the end of the public health emergency, now set to expire in mid-July.
There are many other ways the COVID-19 pandemic has changed healthcare, including:
- Healthcare Workforce: Employees are experiencing widespread burnout, turnover and reductions in engagement.
- Economics: The projected economic impact may alter insurance coverage and consumer health behaviors.
- Mental Health and Chronic Conditions: Behavioral health and chronic conditions management have become increasingly critical.
- Financial Viability: The finances of healthcare organizations, especially rural hospitals, are challenged, and for many, cost-cutting measures are necessary.
- Innovation: Innovative solutions such as remote patient monitoring of COVID-19 patients are more available to address challenges.
- Partnerships: Strategic alliances and linkages are critical for success and economies of scale.
In the face of the ongoing impacts of the pandemic and economic changes, hospital strategies must shift to address the new reality. In my view, the care transformation continuum has never been more important.
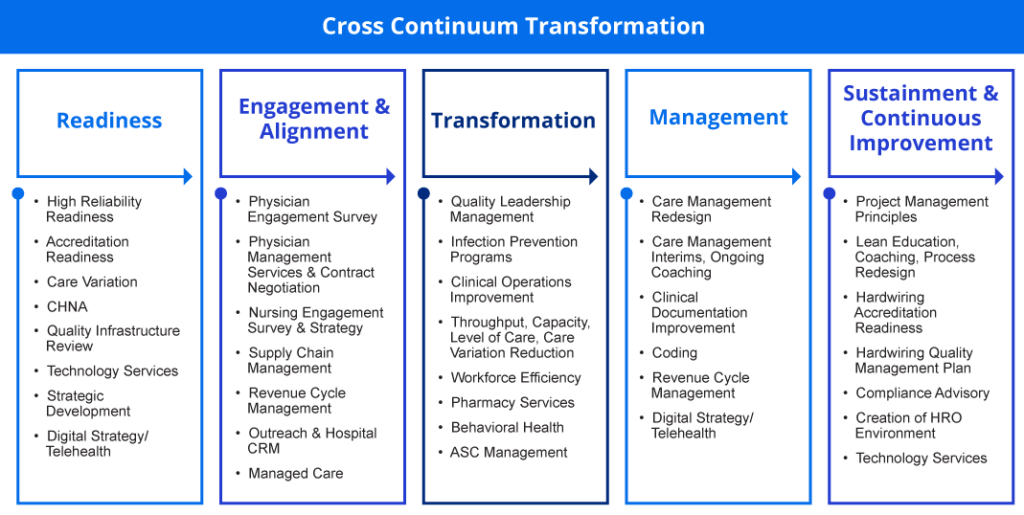
Care Transformation: 5 Areas of Focus
Care transformation is a tremendous topic. To break it down, I say the most effective hospital and health system care transformation initiatives always start with a strategic planning process and focus on five areas:
- Readiness
- Engagement and Alignment
- Transformation
- Management
- Sustainment and Continuous Improvement

Readiness, in short, is enhancing the strategic alignment of care variation reduction with the overall business plan and having a sense of urgency for the next three years. It also is resourcing the organization with reliability and lean healthcare tools.
Other considerations are:
- High Reliability Readiness (Stay tuned for an upcoming blog about this area)
- Accreditation Readiness
- Care Variation
- Community Health Needs Assessment (CHNA)
- Quality Infrastructure Review
- Technology Services
- Strategic Development
- Digital Strategy/Telehealth

At a high level, engagement and alignment are creating confidence that physician agreements and payer contracts will enhance the value equation. It also addresses clinician alignment, culture, burnout and efficiency while balancing supply management and revenue cycle across the continuum.
Other considerations are:
- Physician Engagement Survey
- Physician Management Services and Contract Negotiation
- Nursing Engagement Survey and Strategy
- Supply Chain Management
- Revenue Cycle Management
- Outreach and Hospital Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- Managed Care

In short, transformation is massive process redesign that seeks to deliver patient care at the right time, the right place and at the right price.
Transformation also includes:
- Quality Leadership Management
- Infection Prevention Programs
- Clinical Operations Improvement
- Throughput, Capacity, Level of Care, Care Variation Reduction
- Workforce Efficiency
- Pharmacy Services
- Behavioral Health
- Ambulatory Surgical Center (ASC) Management

At its core, management or care management is patient progression, promoting whole person, patient-centered care using care management and level of care models to align resources across all entities.
- Care Management Redesign
- Care Management Interims, Ongoing Coaching
- Clinical Documentation Improvement
- Coding
- Revenue Cycle Management
- Digital Strategy/Telehealth

Step five, sustainment and continuous improvement, is domain of a very small number of hospitals and healthcare organizations, such as Wooster Community Hospital. After numerous patient and experience awards, Wooster is pursuing a Baldridge Award.
Components of sustainment and continuous improvement are:
- Project Management Principles
- Lean Education, Coaching, Process Redesign
- Hardwiring Accreditation Readiness
- Hardwiring Quality Management Plan
- Compliance Advisory
- Creation of High Reliability Organization (HRO) Environment
- Technology Services
The chart below can serve as a checklist for your organization and help pinpoint gaps that need to be addressed: